iptables
术语解释
- DAST : 目标网络地址转换。 DNAT是一种改变数据包目的ip地址的技术,经常和SNAT联用,以使多台服务器能共享一个ip地址连入Internet,并且继续服务。通过对同一个 ip地址分配不同的端口,来决定数据的流向
- SNAT : 源网络地址转换。这是一种改变数据包源ip地址的技术, 经常用来使多台计算机分享一个Internet地址。这只在IPv4中使用,因为IPv4的地址已快用完了,IPv6将解决这个问题
前言
Linux 系统的防火墙功能是由内核实现的, 在内核版本 ≥2.4 之后包过滤机制是 Netfilter , 而 iptables 只是一个 netfilter 的管理工具
Netfilter 位于 Linux 内核中的包过滤防火墙功能体系, 称为 Linux 防火墙的 内核态, 工作在 OSI 的二层和三层, 构造了五个钩子函数 (Prerouting,Input,Output,Forward,Postrouting) , 通过这五个钩子函数就可以完全控制所有本机发出或者流经本机的数据包
虽然防火墙模块构建在Linux内核,并且要对流经IP层的数据包进行处理,但它并没有改变IP协议栈的代码,而是通过netfilter模块将防火墙的功能引入IP层,从而实现防火墙代码和IP协议栈代码的完全分离。
介绍
iptables 其实是用来管理防火墙的命令工具, 其为防火墙体系提供过滤规则/策略, 决定如何过滤或处理到达防火墙主机的数据包, 称为 Linux 防火墙的 用户态
五个阶段
在前言中提到, Netfilter 提供了五个钩子函数, 对应的是报文处理的五个不同阶段
- Prtrouting : 在数据包进入防火墙之后、路由判断之前对数据包进行修改INPUT在数据包被路由到本地之后,但在用户空间程序看到它之前对数据包进行修改
- Input : 处理入站数据包
- Output : 处理出站数据包
- Forward : 处理转发数据包
- Postrouting : 在进行路由选择后处理数据包
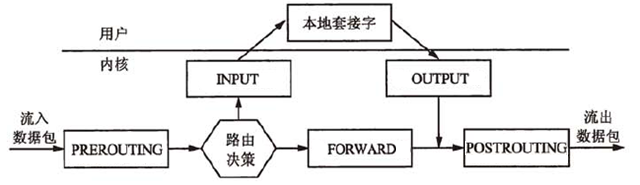
表/链/规则
iptables 的管理主要依赖 表、链、规则三个概念 (类似于数据库的结构), 表是链的容器, 链是规则的容器, 而表又受到 iptables 的管辖
表
主要有五张表, 其中常用的表的为 filter 、nat 、mangle :
- raw 表 : 优先级最高,从而可以对收到的数据包在连接跟踪前进行处理。一但用户使用了RAW表,在 某个链上,RAW表处理完后,将跳过NAT表和 ip_conntrack处理,即不再做地址转换和数据包的链接跟踪处理了.
- filter 表(默认表) : 根据预定于的规则过滤符合条件的数据包, 在 filter 表中只允许对数据包进行接收、丢弃的操作, 无法对数据包进行修改
- nat 表 : 主要是用于网络地址转换 (端口转发), 该表可以实现一对一、一对多、多对多等 NAT 工作
- mangle 表 : 主要用于对指定包的传输特性进行修改。某些特殊应用可能需要改写数据包的一些传输特性,例如更改数据包的 TTL 和 TOS 等
- security 表 : 用于强制访问控制网络规则(例如: SELinux)
对应的每个表中可能包含的阶段如下所以:
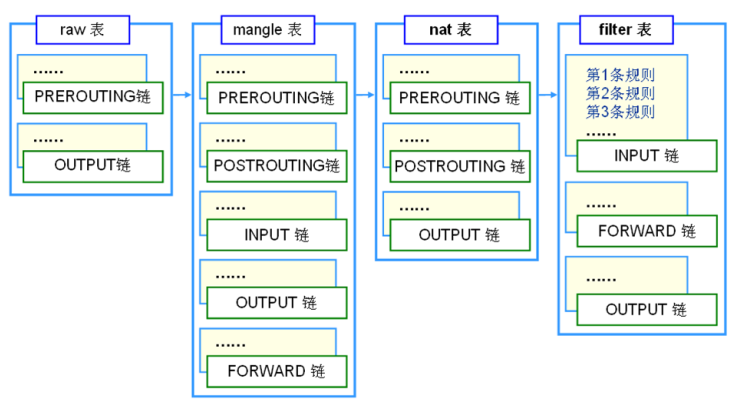
链
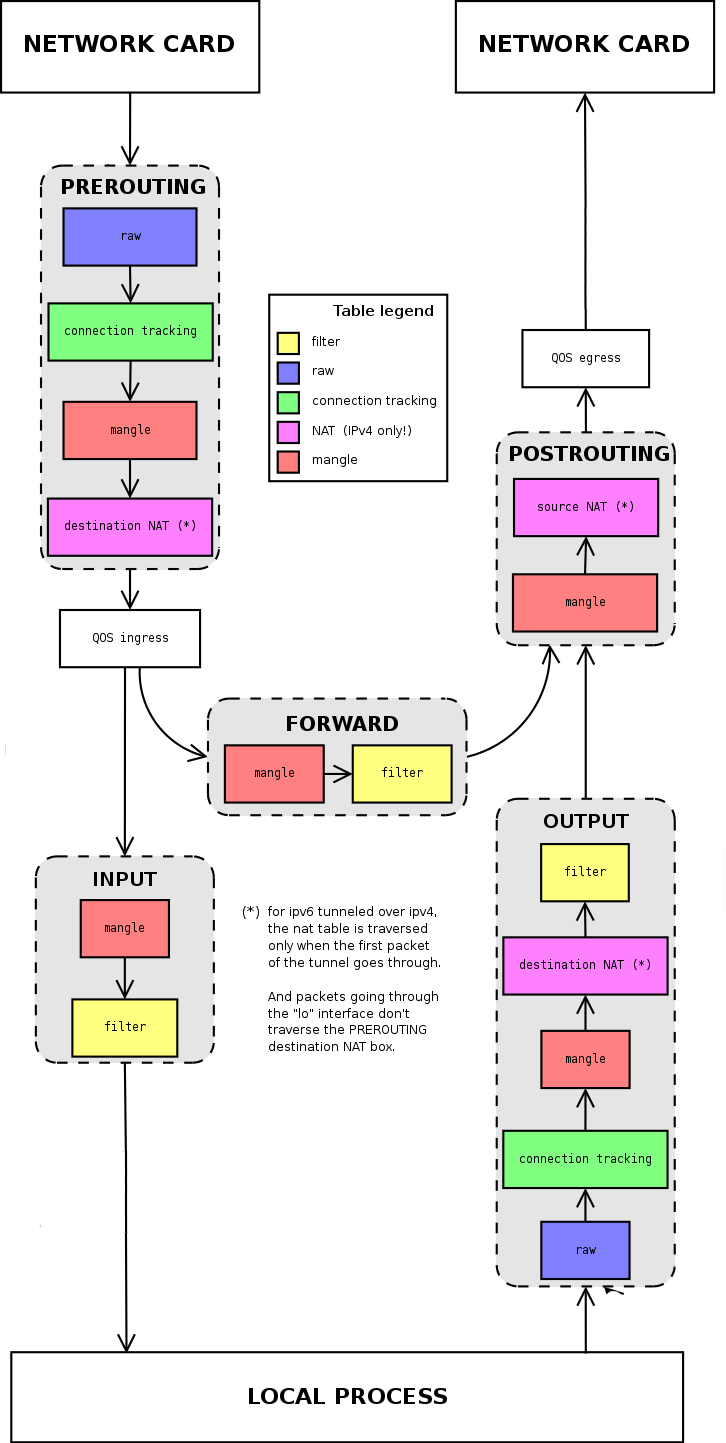
链可以认为是数据包传输的路径, ��对应着报文处理的五个阶段:
- INPUT : 处理入站数据包, 当接收到访问本机地址的数据包时, 应用此链中的规则
- OUTPUT : 处理出站数据包, 当本机向外发送数据包时, 应用此链中的规则
- FORWARD : 处理转发数据包, 当接收到需要通过本机发送给其他地址的数据包时, 应用此链中的规则
- PERROUTING : 在对数据包作路作选择之前, 应用此链中的规则
- POSTROUTING : 在对数据包作路由选择之后, 应用此链中的规则
当一个数据包到达一个链式, 会从第一条规则开始匹配, 如果满足规则条件就会按照规则定义的方法来处理该数据包, 如果都不满足, 就会按照该链预定义的默认策略来处理
规则
规则是一些预定义的数据包过滤条件, 规则存储在内核空间中信息包过滤表中, 数据包每经过一个链时, 系统会根据链中的规则指定的匹配条件来尝试匹配, 一旦匹配成功, 就会按照规则后门指定的处理动作进行处理.
规则分别指定了源地址、目的地址、传输协议、服务类型, 当数据包和规则匹配时, Netfilter 就会根据规则所定义的方式来处理这些数据包, 如放行、拒绝、丢弃等等,配置防火墙的主要规则就是添加、修改和删除这些规则.
规则由匹配条件 和 处理动作 组成, 我们又将 匹配条件, 分为 基本匹配条件 和 扩展匹配条件, 基本匹配条件如:源地址 Source IP,目标地址 Destination IP;扩展匹配条件通常以模块的形式存在,这些模块可以按需安装,源端口 Source Port, 目标端口 Destination Port。
处理动作 也分为基本动作和扩展动作, 下面是一些常用的动作:
- ACCEPT : 允许数据包通过
- DROP : 直接丢弃数据包
- QUEUE : 将数据包移交到用户空间
- RETURN : 停止执行当前链中的后续规则, 并返回到调用链中
- REJECT : 拒绝数据包通过, 必要时会给发送端一个响应的信息, 客户端刚请求就会收到拒绝的信息
- DNAT : 目标地址转换
- SNAT : 源地址转换, 可以解决内网用户使用同一个公网地址上网的问题
- MASQUERADE : SNAT 的一种特殊形式, 适用于动态的、临时会变得 IP 上
- REDIRECT : 在本机作端口映射
- LOG : 记录日志信息,除记录外不对数据包做任何其他操作,仍然匹配下一条规则
数据包流程
使用
┌──(root㉿kali)-[~]
└─# iptables -h
iptables v1.8.10 (nf_tables)
Usage: iptables -[ACD] chain rule-specification [options]
iptables -I chain [rulenum] rule-specification [options]
iptables -R chain rulenum rule-specification [options]
iptables -D chain rulenum [options]
iptables -[LS] [chain [rulenum]] [options]
iptables -[FZ] [chain] [options]
iptables -[NX] chain
iptables -E old-chain-name new-chain-name
iptables -P chain target [options]
iptables -h (print this help information)
Commands:
Either long or short options are allowed.
--append -A chain Append to chain
--check -C chain Check for the existence of a rule
--delete -D chain Delete matching rule from chain
--delete -D chain rulenum
Delete rule rulenum (1 = first) from chain
--insert -I chain [rulenum]
Insert in chain as rulenum (default 1=first)
--replace -R chain rulenum
Replace rule rulenum (1 = first) in chain
--list -L [chain [rulenum]]
List the rules in a chain or all chains
--list-rules -S [chain [rulenum]]
Print the rules in a chain or all chains
--flush -F [chain] Delete all rules in chain or all chains
--zero -Z [chain [rulenum]]
Zero counters in chain or all chains
--new -N chain Create a new user-defined chain
--delete-chain
-X [chain] Delete a user-defined chain
--policy -P chain target
Change policy on chain to target
--rename-chain
-E old-chain new-chain
Change chain name, (moving any references)
Options:
--ipv4 -4 Nothing (line is ignored by ip6tables-restore)
--ipv6 -6 Error (line is ignored by iptables-restore)
[!] --protocol -p proto protocol: by number or name, eg. `tcp'
[!] --source -s address[/mask][...]
source specification
[!] --destination -d address[/mask][...]
destination specification
[!] --in-interface -i input name[+]
network interface name ([+] for wildcard)
--jump -j target
target for rule (may load target extension)
--goto -g chain
jump to chain with no return
--match -m match
extended match (may load extension)
--numeric -n numeric output of addresses and ports
[!] --out-interface -o output name[+]
network interface name ([+] for wildcard)
--table -t table table to manipulate (default: `filter')
--verbose -v verbose mode
--wait -w [seconds] maximum wait to acquire xtables lock before give up
--line-numbers print line numbers when listing
--exact -x expand numbers (display exact values)
[!] --fragment -f match second or further fragments only
--modprobe=<command> try to insert modules using this command
--set-counters -c PKTS BYTES set the counter during insert/append
[!] --version -V print package version.
操作选项 一般为 -j 处理动作 的形式,处理动作包括 ACCEPT、DROP、RETURN、REJECT、DNAT、SNAT 等。不同的处理动作可能还有额外的选项参数,如指定 DNAT、SNAT 动作则还需指定 --to 参数用以说明要装换的地址,指定 REDIRECT 动作则需指定 --to-ports 参数用于说明要跳转的端口。
常用命令
- 帮助信息
- 查看规则信息
- 清除所有规则
- 设置默认规则
- 增加、删除、修改规则
- 开放指定端口
- 持久化规则
iptables --help # 查看 iptables 的帮助
iptables -m 模块名 --help # 查看指定模块的可用参数
iptables -j 动作名 --help # 查看指定动作的可用参数
iptables -nvL
iptables -t nat -nvL
# 显示规则序号
iptables -nvL INPUT --line-numbers
iptables -t nat -nvL --line-numbers
iptables -t nat -nvL PREROUTING --line-numbers
# 查看规则的原始格式
iptables -t filter -S
iptables -t nat -S
iptables -t mangle -S
iptables -t raw -S
iptables -F # 清空表中所有的规则
iptables -X # 删除表中用户自定义的链
iptables -Z # 清空计数
iptables -t nat -F
iptables -t nat -X
iptables -t mangle -F
iptables -t mangle -X
iptables -t raw -F
iptables -t raw -X
iptables -t security -F
iptables -t security -X
iptables -P INPUT DROP # 配置默认丢弃访问的数据表
iptables -P FORWARD DROP # 配置默认禁止转发
iptables -P OUTPUT ACCEPT # 配置默认允许向外的请求
# 增加一条规则到最后
iptables -A INPUT -i eth0 -p tcp --dport 80 -m state --state NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT
# 注:以下几条操作都需要使用规则的序号,需要使用 -L --line-numbers 参数先查看规则的顺序号
# 添加一条规则到指定位置
iptables -I INPUT 2 -i eth0 -p tcp --dport 80 -m state --state NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT
# 删除一条规则
iptabels -D INPUT 2
# 修改一条规则
iptables -R INPUT 3 -i eth0 -p tcp --dport 80 -m state --state NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT
# 允许本地回环接口(即运行本机访问本机)
iptables -A INPUT -i lo -j ACCEPT
# 允许已建立的或相关连接的通行
iptables -A INPUT -m state --state ESTABLISHED,RELATED -j ACCEPT
# 允许所有本机向外的访问
iptables -A OUTPUT -j ACCEPT
# 允许 22,80,443 端口的访问
iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 22 -j ACCEPT
iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dports 80,443 -j ACCEPT
# 如果有其他端口的需要开放,则同上
iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 8000:8010 -j ACCEPT
# 允许 ping
iptables -A INPUT -p icmp -m icmp --icmp-type 8 -j ACCEPT
# 禁止其他未允许的规则访问
iptables -A INPUT -j REJECT
iptables -A FORWARD -j REJECT
# 注:以上操作需要安装顺序,确保规则顺序正确
目的地址转换,首先需要在开启中开启转发功能(源地址转换也需要开启):
echo 1 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward
# 把从 eth0 进来要访问 TCP/80 的数据包的目的地址转换到 192.168.1.18
iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -p tcp -i eth0 --dport 80 -j DNAT --to 192.168.1.18
# 把从 123.57.172.149 进来要访问 TCP/80 的数据包的目的地址转换到 192.168.1.118:8000
iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -p tcp -d 123.57.172.149 --dport 80 -j DNAT --to 192.168.1.118:8000
源地址转换
# 最典型的应用是让内网机器可以访问外网:
# 将内网 192.168.0.0/24 的源地址修改为 1.1.1.1 (可以访问互联网的机器的 IP)
iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -s 192.168.0.0/24 -j SNAT --to 1.1.1.1
# 将内网机器的源地址修改为一个 IP 地址池
iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -s 192.168.0.0/24 -j SNAT --to 1.1.1.1-1.1.1.10
# 保存当前规则
iptables-save > iptables.20190721
# 恢复备份规则
iptables-restore < iptables.20190721